Rapid Review: Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome

Reviewed January 2024
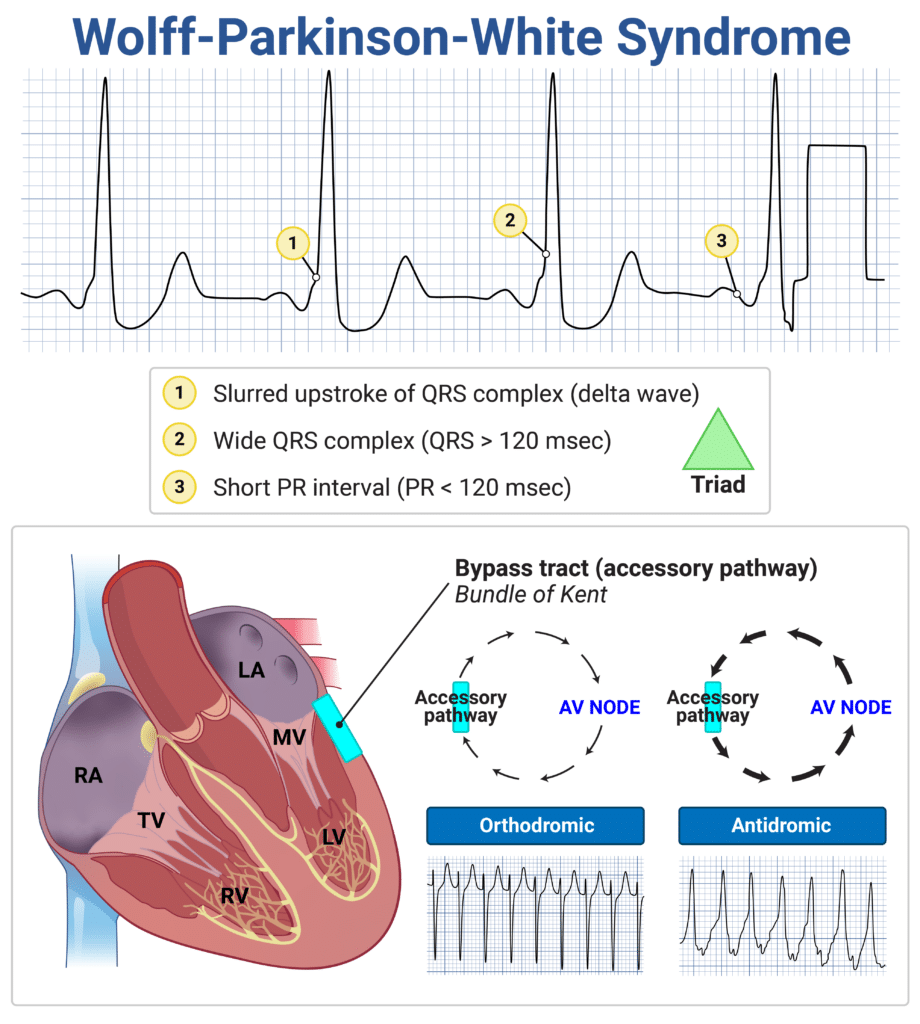
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) Syndrome
- ECG will show short PR interval, delta wave, wide QRS
- Most commonly caused by an accessory pathway (bundle of Kent) connecting atria to ventricles, bypassing AV node
- Acute treatment:
- Orthodromic (narrow complex): vagal maneuvers, AV nodal blockers (adenosine, beta-blocker, calcium channel blocker)
- Antidromic (wide complex): procainamide
- Synchronized cardioversion for hemodynamically unstable patients
- Definitive treatment is radiofrequency ablation
Sample question:
A 23-year-old man presents to your clinic with intermittent episodes of chest discomfort, heart palpitations, and decreased exercise tolerance. Which of the following ECG findings would most strongly suggest a diagnosis of Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome?
Get Free Access and Join Thousands of Happy Learners
Categories: Adult-Gerontology Primary Care , Certified , Certified Emergency Nurse , Clinical Year , Didactic Year , Emergency Medicine , Emergency Nurse Practitioner , Family Medicine , Family Nurse Practitioner , Internal Medicine , Pediatric Emergency Medicine , Pediatric Primary Care , Rapid Review ,





Comments (0)