Podcast Ep 27: Hyperkalemia, Blast Injuries & More
It is during our darkest moments that we must focus to see the light.
-Aristotle
Welcome back to Episode 27 and a big welcome to all the new interns who are only about 1 week into residency! We hope you find Roshcast to be easy to listen to and helpful in your education. As we have said from the outset, we want this to be as high-yield as possible to not only improve your in-training scores but also improve your care at the bedside. We are open to any suggestions, so please reach out.
Let’s get warmed up with a rapid review – this week, we are going over some HIV-related illnesses.

- Toxoplasmosis is rarely seen with CD4 > 200. Be concerned in those with CD4 < 100.
- Toxoplasmosis is transmitted through cat feces. It is treated with pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine, and folinic acid.
- The classic X-ray finding for PJP pneumonia is diffuse interstitial infiltrates in a “bat wing” appearance.
- In PJP pneumonia, if the PaO2 is less than 70 or the A-a gradient is greater than 36, treat with steroids in addition to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.
Now onto this week’s podcast
Question 1
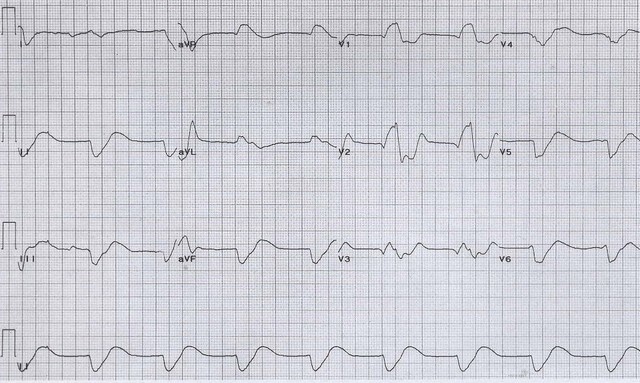
A 67-year-old man with hypertension and end-stage renal disease presents after an incomplete dialysis session secondary to shortness of breath. His vital signs are BP 110/95, HR 65, RR 22, T 37.3°C, and oxygen saturation 99% on 2L NC. You obtain the ECG shown above, which shows a widened QRS, almost resembling a sine wave. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in this patient’s management?
A. Calcium gluconate
B. Cardiology consultation
C. Defibrillation
D. Transcutaneous pacing
Question 2
EMS calls notifying you that there is a mass casualty situation. There was an explosion at a construction site and they will be bringing 20 ambulatory, asymptomatic patients to your emergency department. After checking airway, breathing and circulation, what test, if normal, would allow you to rapidly discharge patients?
A. Abdominal ultrasound
B. Ophthalmoscope evaluation of the eye
C. Otoscope evaluation of tympanic membranes
D. Oxygen saturation
Question 3
A 42-year-old woman with sickle cell anemia presents to the ED complaining of unilateral knee pain. You are worried she might have septic arthritis. Which of the following organisms is most likely to be responsible?
A. Pasturella multocida
B. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
C. Salmonella spp.
D. Staphylococcus aureus
Question 4
In which of the following spondyloarthropathies is uveitis the most common extra-articular manifestation?
A. Ankylosing spondylitis
B. Fibromyalgia
C. Psoriatic arthritis
D. Reactive arthritis
Question 5
At which location is the pediatric airway the narrowest?
A. Cricoid
B. Epiglottis
C. Pharynx
D. Vocal cords
Question 6
A 29-year-old man presents to the ED with partial-thickness burns to his entire back and right arm. The patient weights 70 kg. Based on the Parkland formula, how much crystalloid solution is required in the first 24 hours?
A. 1,260 mL
B. 10,080 mL
C. 5,040 mL
D. 7,560 mL

- EKG changes seen in patients with hyperkalemia include peaked T waves, QRS widening, dropped P waves, and bradycardia.
- Temporizing measures for managing hyperkalemia include calcium, insulin and glucose, sodium bicarbonate, and albuterol.
- Furosemide and dialysis can be used to permanently remove potassium from the body.
- For blast injuries, make sure to examine the tympanic membranes. They are damaged at lower pressures than other parts of the body.
- Primary blast injuries occur from blast overpressure. Secondary blast injuries are caused by flying debris. Tertiary blast injuries are caused by victims being thrown. And lastly, quaternary blast injuries are caused by environmental hazards caused by the explosion.
- The most common cause of septic arthritis is Staphylococcus aureus in adults and children over 2, except for sexually active younger adults, in which case Neisseria gonorrhoeae is more common.
- On joint aspirate of a septic joint, the white blood cell count is typically greater than 50,000 and the aspirate appears purulent. Remember that if clinical suspicion is high, start antibiotics, consult an orthopedist early, and defer to the gram stain and culture for definitive diagnosis.
- The most common extra-articular manifestation of ankylosing spondylitis is uveitis.
- The narrowest part of the pediatric airway is the cricoid.
- As compared to the adult airway, the pediatric airway has a proportionally smaller larynx, which is more anterior, the epiglottis is longer and narrower, the tongue is proportionally larger, the neck is typically shorter, and the adenoids are often larger.
- The pediatric endotracheal tube should be placed to a depth of 3 x the endotracheal tube size.
- The parkland formula can be calculated by the formula 4 x % TBSA burned x weight (kg). Give the first half in the first 8 hours and the second half over the next 16 hours.
- Although, the parkland formula is a good guide, fluid resuscitation in burns should ultimately be guided by vital signs and urine output. In children, target 1–2 mL/kg/hr, and in adults, target 30 mL/hr.
That wraps up Episode 27. From blast injuries to hyperkalemia, we have covered the entire spectrum of emergency medicine this week. Hope you enjoyed. Do not forget to listen for the trauma phone ring tone in the coming weeks for a chance to win a Rosh Review Subscription. Remember to tweet @Roshcast or email Roshcast@roshreview.com the exact time when you hear the ring to win the prize.
Until next time,
Jeff and Nachi





Comments (0)