Podcast Ep 8: Pneumonia, Herpes Zoster, Lung Ultrasound & More
In the end the great truth will have been learned, that the quest is greater than what is sought, the effort finer than the prize, or rather that the effort is the prize, the victory cheap and hollow were it not for the rigor of the game.
-Justice Benjamin Cardozo
Welcome back to episode 8! With Thanksgiving behind us, let’s keep up the momentum, as the In-Training Exam is right around the corner. Here is a sneak peek into the category breakdown established by ABEM for the ITE.
Roshcast episodes are 10–15 minutes long so you can focus on a few topics at a time without feeling overwhelmed. The short duration of each episode also allows you to go back and review episodes you may have missed or want to reinforce.
We begin each episode with a quick Rapid Review of the previous week’s highlights.

- Rh immunoglobulin administration can be delayed up to 72 hours. The correct dose is 50 mcg for those less than 12 weeks gestation and 300 mcg for those 12 weeks and over.
- Haloperidol and other typical antipsychotics can cause a dystonic reaction. The treatment is either benztropine or diphenhydramine. 50% of reactions occurring within 48 hours of administration and 90% occur within 5 days.
- The target pH for eye irrigation should be between 7.0–7.2, but do not delay irrigation to confirm a staring pH.
- Sulfonylureas commonly cause recurrent hypoglycemia as they stimulate the islet beta cells to secrete more insulin, increase the sensitivity of peripheral tissues to insulin, and have a prolonged half-life.
Now to this week’s podcast
Question 1
Which of the following patients requires emergent consultation with an orthopedic specialist?
A. A 36-year-old woman with a femur fracture and distal cyanosis
B. 58-year-old man with extension-based chronic low back pain and leg numbness
C. 75-year-old ambulatory woman with a tibial osteosarcoma
D. An 18-year-old man with a reduced sacral ala fracture and BP 130/86
Question 2
A 12-year-old boy presents to the ED with headache, vomiting, and lethargy for two days. He had a ventriculoperitoneal shunt placed for hydrocephalus one year ago. What is the most likely cause of his shunt malfunction?
A. Abdominal pseudocyst formation
B. Choroid plexus obstruction
C. Loculation
D. Mechanical failure
E. Slit ventricle syndrome
Question 3
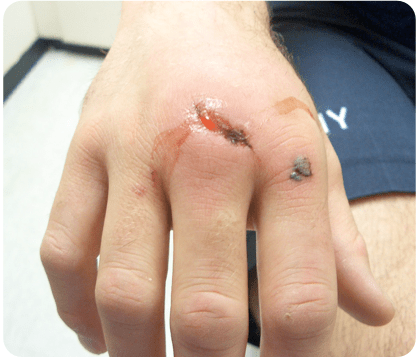
A 25-year-old man presents to the emergency department after being in an altercation at a music concert. On exam, you note the findings seen above. Which of the following organisms is of most concern?
A. Capnocytophaga canimorsus
B. Cercopithecine herpesvirus
C. Eikenella corrodens
D. Pasteurella multocida
Question 4
Which of these children with hematuria needs admission to the hospital?
A. A 10-year-old boy with recent sore throat treated with amoxicillin, tea-colored urine, and normal urine output; UA shows microscopic hematuria and proteinuria; blood tests are normal
B. A 12-year-old girl with lower abdominal pain, dysuria, urgency, frequency, and pink urine; UA shows microscopic hematuria, > 50 WBCs/hpf, + leukocyte esterase, + nitrites; urine pregnancy test is negative
C. A 6-year-old boy with nausea, vomiting, bloody diarrhea, and decreased urine output; UA shows microscopic hematuria and hyaline casts; blood tests show a high WBC count, low hemoglobin, and low platelets
D. An 8-year-old girl with diffuse mild edema, tea-colored urine, and normal urine output; UA shows microscopic hematuria and proteinuria; blood tests show a normal WBC count, hemoglobin, and platelets but low protein
Question 5
Which of the following is a cyanotic heart lesion?
A. Atrial septal defect
B. Patent ductus arteriosus
C. Tricuspid atresia
D. Ventricular septal defect
Question 6
A 68-year-old man presents to the ED after a fall down 12 stairs. His only medication is warfarin, which he takes for atrial fibrillation. On physical exam, you note a large parietal scalp hematoma. His noncontrast computed tomography scan of the head is shown above. His INR is 4.5. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
A. Cryoprecipitate
B. Fresh frozen plasma
C. Packed red blood cells
D. Platelets

- Emergent orthopedics consultation is needed for any fracture with neurovascular compromise, suspected compartment syndrome, all open fractures, and all displaced unstable fractures and irreducible fractures.
- VP shunt obstruction occurs proximally more frequently than distally.
- Proximal VP shunt obstruction occurs due to choroid plexus obstruction or increased protein within the CSF.
- Distal VP shunt obstruction occurs due to abdominal pseudocyst formation, which typically presents with abdominal pain due to the large size of the cyst.
- With respect to VP shunt malfunction, slit ventricle syndrome occurs when the ventricles are over drained and they collapse, obstructing the proximal shunt orifice. With the reaccumulation of fluid, the obstruction is relieved. Patients typically present with cyclical symptoms.
- In treating patients with fight bites, we are concerned for Eikenella contamination. In fight bites overlying the metacarpal, a hand surgery consultation is necessary.
- In human bites, amoxicillin-clavulanate is typically the first-line antibiotic of choice. For established infections, IV antibiotics such as ampicillin-sulbactam, cefoxitin, or piperacillin-tazobactam may be used.
- For a child with mild to moderate edema, with a normal blood pressure and no respiratory symptoms, the child can typically be discharged home with outpatient nephrology follow up. The treatment is typically corticosteroids.
- Hematuria with hearing loss is associated with Alport syndrome. Hematuria and hemoptysis is associated with Goodpasture’s syndrome.
- There are five important cyanotic congenital heart lesions to remember. Remember the numbers 1 to 5. One is for truncus arteriosus, in which two vessels join to make one. Two is for transposition of the great vessels in which the two great vessels are switched. Three is for tricuspid atresia. Remember three for TRIcuspid. Four is for the four defects of tetralogy of Fallot. Lastly, five is for the five letters of total anomalous pulmonary vascular return.
- Atrial septal defects, patent ductus arteriosus, and ventricular septal defects are all acyanotic heart lesions, or lesions with left to right shunt. Symptomatic children with such lesions typically present with congestive heart failure by 6 months of life.
- For any patient on warfarin with a life-threatening bleed, FFP, PCC, or recombinant factory, 7a should be given.
- For a patient on aspirin with a life-threatening bleed, DDAVP should be given in addition to platelets.
Until next time,
Jeff and Nachi
P.S. If you like Nachi and Jeff’s content, remember to check out Rosh Review’s emergency medicine qbank with thousands of high yield questions, explanations, images, audio, and video teaching files.





Comments (0)