Podcast Ep 48: Pediatric Back Pain, Lateral Canthotomy, & More

Success is not final, failure is not fatal: it is the courage to continue that counts.
–Winston Churchill
Welcome back to RoshCast for Episode 48! We’re going to jump right into questions this week. Remember to send us feedback for any changes you would like to see at roshcast@roshreview.com.
Question 1
An 8-year-old previously healthy boy presents with back pain and fever for 4 days. He complains of pain in the low back, which is increased with bending or twisting. The pain radiates down into his left leg. He denies trauma. Physical exam is remarkable only for tenderness to palpation over the lumbar spine. What management is indicated
A. Ibuprofen and follow up with his pediatrician
B. MRI of the lumbar spine
C. Plain radiographs of the lumbar spine
D. Urinalysis
Question 2
A 40-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after being assaulted during a bar fight. He has proptosis of the right eye with a measured intraocular pressure of 50 mm Hg. A lateral canthotomy is started. Once the Kelly clamp is released from the lateral canthus, what is the appropriate next step?
A. Clamp the medial canthus
B. Cut the inferior crus of the lateral canthal tendon
C. Cut the superior crus of the lateral canthal tendon
D. Recheck intraocular pressure
Question 3
A 25-year-old man presents to the emergency department after sustaining burns to the hands, legs, and chest after falling into a bonfire. On physical examination, there are partial-thickness burns on the upper half of the anterior torso along with the bilateral palms of the hands and bilateral anterior legs. He weighs 70 kg. You begin to initiate fluid resuscitation using the Parkland formula. How much fluid should this patient receive in the first eight hours?
A. 10,640 mL
B. 4,060 mL
C. 5,320 mL
D. 8,120 mL
Question 4
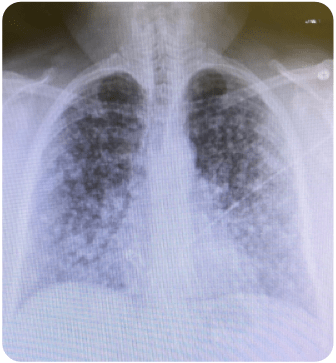
A 64-year-old man presents to the emergency department with cough and shortness of breath that has progressively been worsening over the last several weeks. He has also been more fatigued and is unable to get around the house anymore. He denies fever and night sweats. He has a past medical history of hypertension and takes lisinopril daily. He is an immigrant from Argentina where he used to work as a miner. He denies tobacco use. What is the most likely diagnosis based on this chest radiograph?
A. Histoplasmosis
B. Miliary tuberculosis
C. Pneumoconiosis
D. Sarcoidosis
Question 5
A 53-year-old man presents with numbness to his right hand for three to four months. He states that he has numbness with waking up in the morning, which gets better when he shakes his hands. The patient indicates numbness to his first, second, and third digits on the right hand. Which of the following tests is most sensitive for this diagnosis?
A. Finkelstein test
B. Median nerve compression test
C. Phalen test
D. Tinel sign
Question 6
A young man is involved in a motor vehicle collision and sustains a severe head injury. In the ED, his GCS is 7. His blood pressure is 115/70 mm Hg and heart rate is 85 beats per minute. His pupils are 3 mm and equal and reactive to light. You intubate the patient and place him on a mechanical ventilator. The FAST ultrasound is negative and there are no other obvious injuries. Which of the following is the most important principle to follow in the management of this patient?
A. Administer mannitol
B. Avoid hypotension
C. Hyperventilation
D. Initiate induced hypothermia

- Discitis presents with severe localized radiating pain. The lumbar spine is most commonly involved, and treatment is with IV antibiotics.
- A lateral canthotomy is performed to relieve intraocular pressure from a retrobulbar hematoma or a postseptal hemorrhage. It is done by cutting the inferior crus of the lateral canthal tendon.
- The Parkland Formula is used to determine the volume of fluid required for resuscitation of burn patients. It is 4 mL x body weight in kg x % total body surface area of the burn. Half of this fluid is given within the first 8 hours and then other half over the next 16 hours.
- Pneumoconiosis is a restrictive lung disease that can be caused by inhalation of dust, often in mines. It presents with bilateral ground glass opacities on Chest X-ray.
- The Median Nerve Compression Test is the most sensitive test for confirming carpal tunnel syndrome. It consists of direct pressure application to the median nerve at the carpal tunnel.
- Hypotension and hypoxia have both been shown to have a devastating effect on the outcome of patients with traumatic brain injury.
That wraps up RoshCast Episode 48! Be sure to also check out the rest of the Rosh Review Blog for questions from prior episodes, related images and tables, and bonus teaching points. There are also tons of other great free resources to help prepare you for the boards and the wards. Don’t forget to follow us on twitter @RoshCast. And you can always email us at RoshCast@RoshReview.com with any feedback, corrections, or suggestions.
You can also help us pick questions by identifying ones you would like us to review. Write “RoshCast” in the submit feedback box as you go through the question bank. Lastly, if you have a minute, make sure to rate us and leave comments on iTunes to help spread the word about RoshCast.
Megha and Nachi





Comments (0)