Rapid Review: Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn

Reviewed January 2024
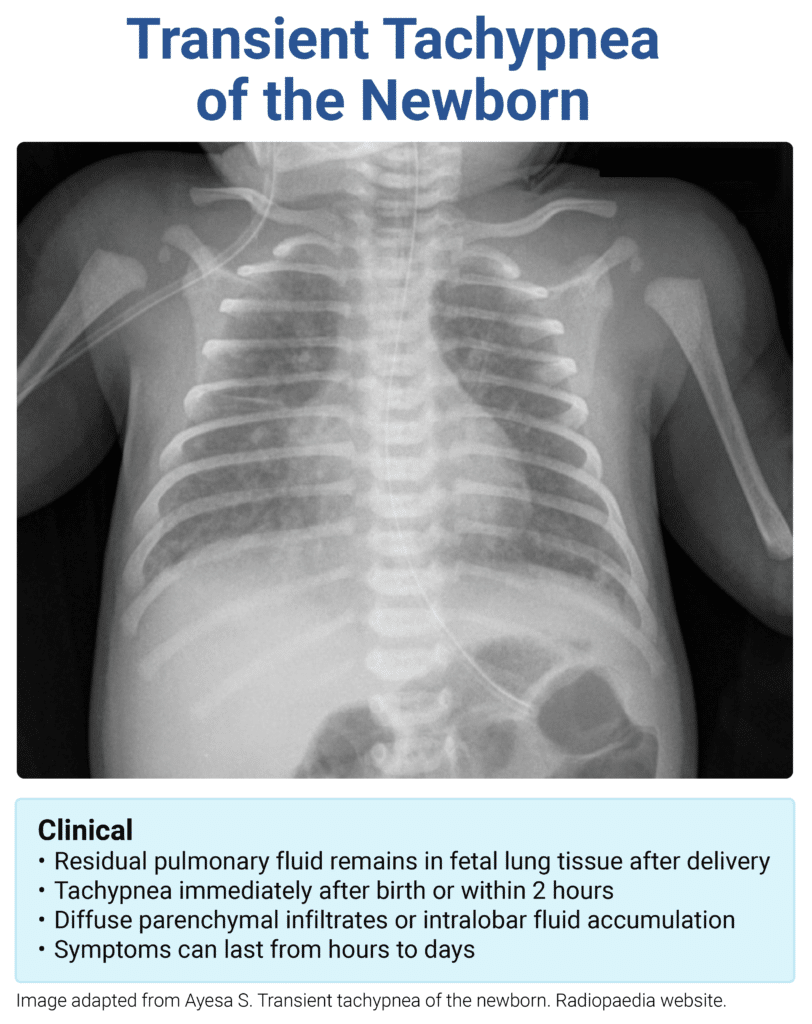
Transient Tachypnea of the Newborn
- Most common cause of neonatal respiratory distress
- RF: C/S, IDM, maternal obesity, precipitous delivery
- Cause: delayed clearance of fetal lung fluid
- PE: early onset tachypnea, nasal flaring, retractions, and hypoxia
- CXR: parenchymal infiltrates and fluid in the pulmonary fissures
- Tx: supportive, self-resolving within 72 hours
Sample question:
A 3,500 g male infant is born via scheduled cesarean delivery at 41 weeks of gestation to a G2P2 mother with a past medical history of asthma. He develops mild respiratory distress shortly after birth. Vital signs include T 37.2°C, P 140 bpm, R 75/minute, and SpO2 95% on room air. Physical examination reveals nasal flaring, mild intercostal retractions, and cyanosis. Auscultation of the lungs is normal and heart sounds are normal. Chest radiograph reveals hyperinflation, a flattened diaphragm, and prominent vascular markings in a sunburst pattern originating from the hilum. Supplemental oxygen is provided and symptoms resolve within four hours. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?





Comments (0)