Emergent & Urgent Care Module For the ABFM Certification Exam Is Now Ready
Introducing the new ABFM Emergent & Urgent Care Content-Specific Module, available to Family Medicine residents, residency programs, and practicing physicians. This module is best suited for Family Medicine physicians looking for a focused, high-yield Qbank review for ABFMs Content-Specific Modules required during the certification exam. This content is novel, and not included in Rosh Review’s main Family Medicine Qbank or mock exams.
Family Medicine programs who subscribe to Rosh Review also gain access to the Content-Specific Modules in their PD Dash.
Categories include:
- Resuscitation
- Environmental
- Poisoning
- Trauma
- Exacerbation of chronic illnesses
- Acute illnesses
Content is organized by task:
- History and Physical
- Diagnostic studies
- Diagnosis
- Health maintenance
- Clinical intervention
- Clinical therapeutics
- Scientific concepts
Here is an example:
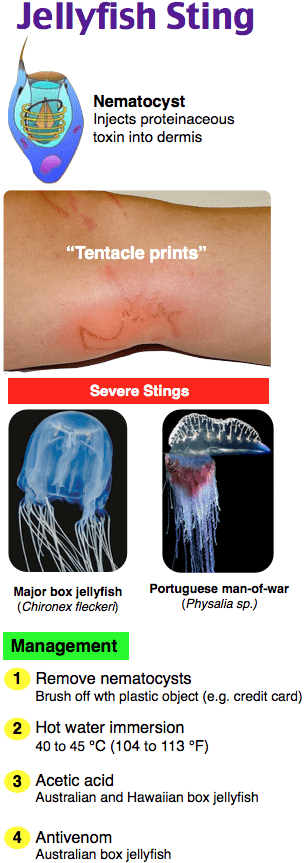
A 37-year-old woman is walking on a beach while vacationing in Hawaii. She is stung by a jellyfish. After removing the nematocysts, which of the following should she apply to the area of the jellyfish sting?
A. Acetic acid
B. Alcohol
C. Fresh water
D. Pressure immobilization bandaging
Answer A
Jellyfish tentacles contain from a few thousand to several billion nematocysts, which are hollowed capsules containing a tightly coiled thread immersed in venom. When the thread tubules evert, the venom is injected on the outside of the thread tube. Nematocysts are discharged onto the skin within a fraction of a second and can do so even when separated or if the organism is dead. Certain types of jellyfish, especially near Australia, can produce massive envenomation resulting in severe systemic symptoms and sometimes death as a result of cardiac asystole, usually within a few minutes. Acetic acid 5% (household vinegar) should be applied to the wound for 30 seconds to prevent further discharge of unfired nematocysts remaining on the skin. Salt water or tweezers also can be used to remove the nematocysts. Oral and topical analgesics, hot water, and ice packs are used to reduce pain. The pain is self-limiting, lasting two to three days. For prevention, a skin inhibitor cream can be applied before going in the water. It consists of a waterproof sunscreen that contains octyl methoxycinnamate and zinc oxide. While not eliminating the stings, it significantly reduced their frequency and severity. Full-body diving suits are almost totally effective in preventing all jellyfish stings.
Discharge of the jellyfish venom is triggered by mechanical stimuli (such as skin rubbing or tentacle traction) and sudden increase in the osmotic pressure of the capsular fluid. Therefore, alcohol (B), fresh water (C), and pressure immobilization bandaging (D) should be avoided, as these treatments could massively discharge additional venom from the remaining nematocysts. Other solutions such as urine and rubbing with sand should be avoided for the same reason.
One Step Further question:
For which deadly jellyfish stings is antivenom available?
Answer:
Box jellyfish, found in the Indo-Pacific region and northern Australia.
Since these categories and tasks are integrated into our improved performance and feedback page, you have access to robust data to help you fine-tune your studying and resources to help increase your Family Medicine Certification Exam score by 100 points.
Or visit the main Family Medicine Qbank page to learn about our ABFM Certification Qbank
Study on…
The Rosh Review Team
A bolus of confidence. A lifetime of knowledge.





Comments (0)