Aligned with the National Board of Medical Examiners format. Authored & peer-reviewed by faculty, clinicians, and clerkship directors.
Each question is written to resemble the format and topics on the exam, meaning you won’t see any negatively phrased questions, no “all of the following except,” no “A and B”…you know what we mean. Most importantly, all questions include selective distractors (incorrect answer choices), which will help you think critically.
Understanding why an answer choice is incorrect is just as important as knowing why one is correct. That’s why every Rosh Review question includes detailed explanations for the correct and incorrect answer choices. These comprehensive summaries link the most important components of a topic—from risk factors to diagnostics and treatment—giving you the context to build relationships between them.
Custom illustrations and tables help further clarify the core concepts. When information is presented visually, you can focus on meaning, easily reorganize and group similar ideas, and make better use of your memory.
Your personal analytics allow you to see your progress at all times, so you can create an efficient and effective learning strategy and stay on pace with your plan.
After each explanation is a straightforward question with a simple, memorizable answer that reinforces the corresponding topic.
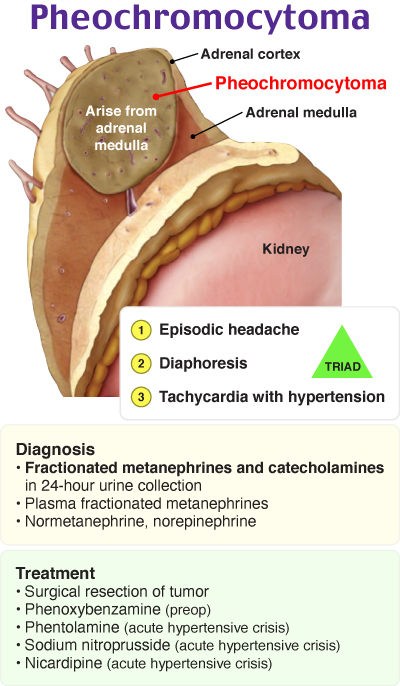
Pheochromocytoma
These bulleted reviews focus on condensed, high-yield concepts about the main topic, from patient presentation to preferred management.
“I just received comfortably above passing score on the Initial Certification Exam! When I started using Rosh Review last year for the In-Service, my scores started rising considerably. Thanks again!”

Matthew DeAugustinis, MD
Attending Physician