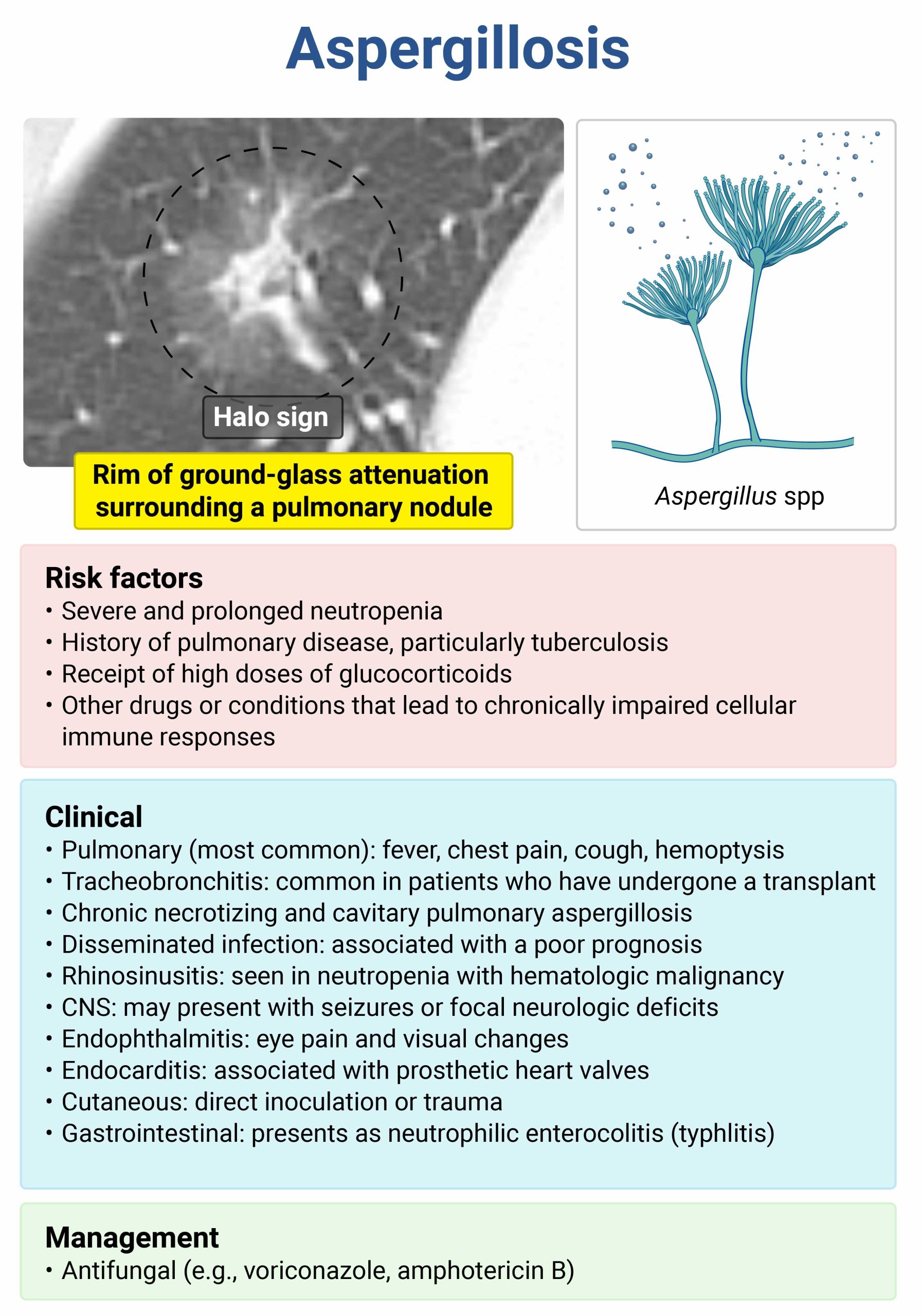
A 17-year-old girl with leukemia who is undergoing chemotherapy presents with fever, cough, hemoptysis, and pleuritic chest pain. Bronchoscopy with biopsy reveals narrow, septated hyphae with dichotomous acute angle branching. Which of the following organisms is likely to be isolated on culture?
A Aspergillus B Candida C Pseudomonas D StaphylococcusThis girl’s biopsy is characteristic of invasive Aspergillus infection. Risk factors for invasive pulmonary aspergillosis include prolonged, severe neutropenia that may result from chemotherapy, treatment with high-dose glucocorticoids, or other medications or diseases that may cause immunosuppression. The constellation of fever, pleuritic chest pain, and hemoptysis is considered the hallmark of infection, but neutropenic patients may present with only fever.
Chest X-ray often overlooks the focal lesions of aspergillosis, particularly in early disease, but chest CT may reveal one or several cavitary or noncavitary nodules, segmental or patchy consolidation, or peribronchial infiltrates. In neutropenic patients, there is often hemorrhage into the surrounding tissue, resulting in the “halo sign,” in which nodules have surrounding ground-glass infiltrates. Often serum biomarkers, including galactomannan and beta-D-glucan assays, may assist with diagnosis. Sputum culture is also diagnostic. Patients for whom diagnosis is not clear after these methods may undergo bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage and possibly a lung biopsy.
Invasive Candida (B) infection may also occur in immunocompromised hosts. It has a varied presentation, from mild symptoms to sepsis, but common features include distinctive eye and skin lesions and muscle abscesses.
Pseudomonas (C), an aerobic gram-negative bacillus, is also a concern in a febrile neutropenic patient. Empiric treatment for high-risk children who have chemotherapy-induced neutropenia should include an agent that can treat Pseudomonas, such as cefepime, meropenem, or piperacillin-tazobactam.
Staphylococcus (D), including coagulase-negative staphylococci and Staphylococcus aureus, are among the most common gram-positive organisms isolated in patients with fever and neutropenia but in this case the biopsy was not suggestive of a gram-positive bacteria.
Written and designed to help you understand the core concepts. Questions are just like you'll see on the actual exam, while explanations and illustrations focus on the essential information.
Get tailored performance insights based on your Qbank and the exam you're preparing for. Whether it's projected scores, pass probability, or both, your dashboard highlights strengths, pinpoints areas to improve, and helps you focus where it matters most.
“The most beautiful teaching images on the planet” help you further reinforce the core concepts. Visuals allow you to focus on meaning, group similar ideas, and make better use of your memory (and they're great to look at, too).
Personalized instruction from Content Education Experts who have been where you are and will help teach, uplift, and inspire you. It's like having a personal tutor!
Messages are answered by actual people—not bots—whose goal is to help and support you (with cheetah-like speed). Anything you need, we're here.
Want to revisit a helpful image or explanation? The search feature can help you quickly locate it. But you won't find any spoilers here—it searches content you've already seen.