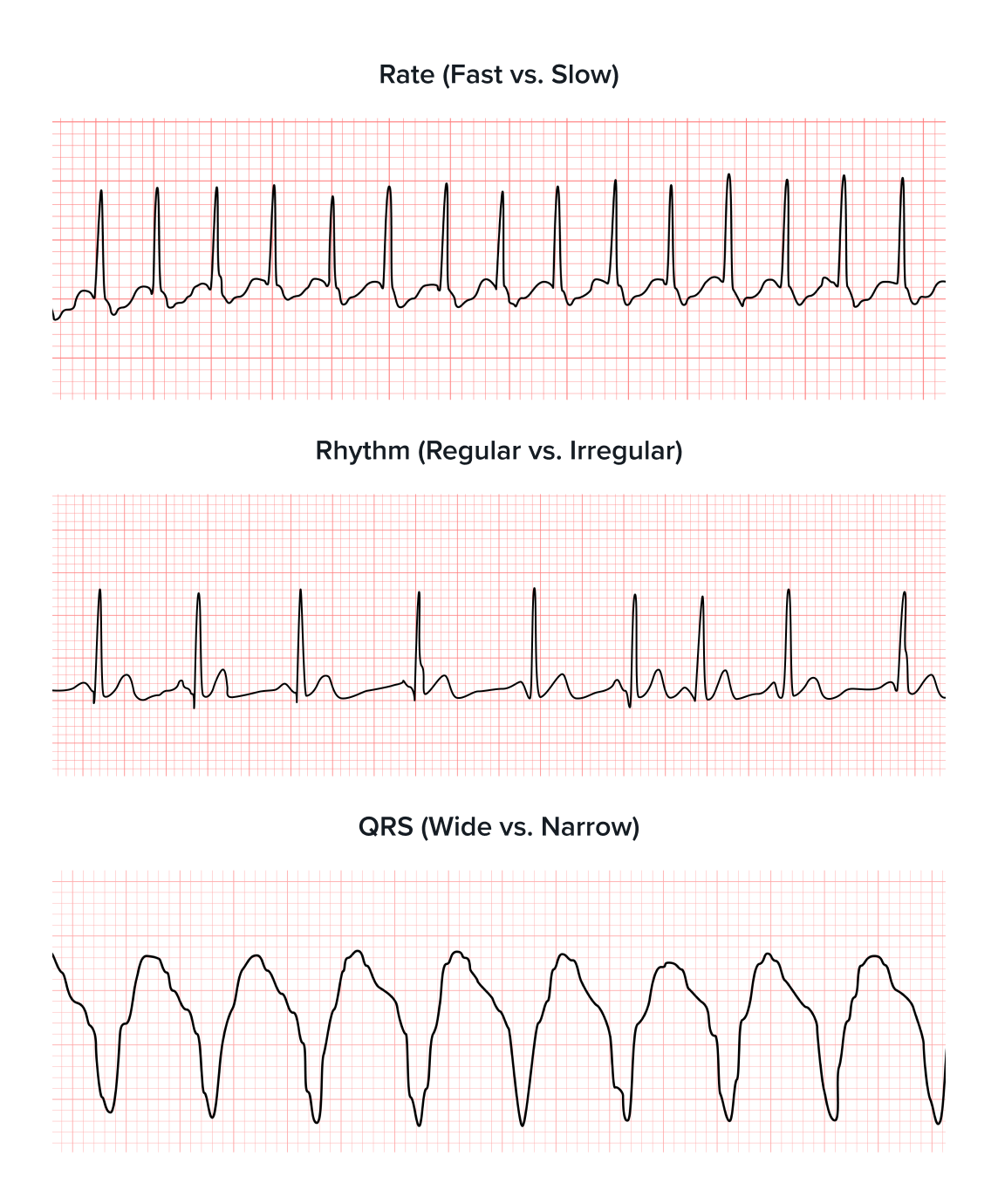
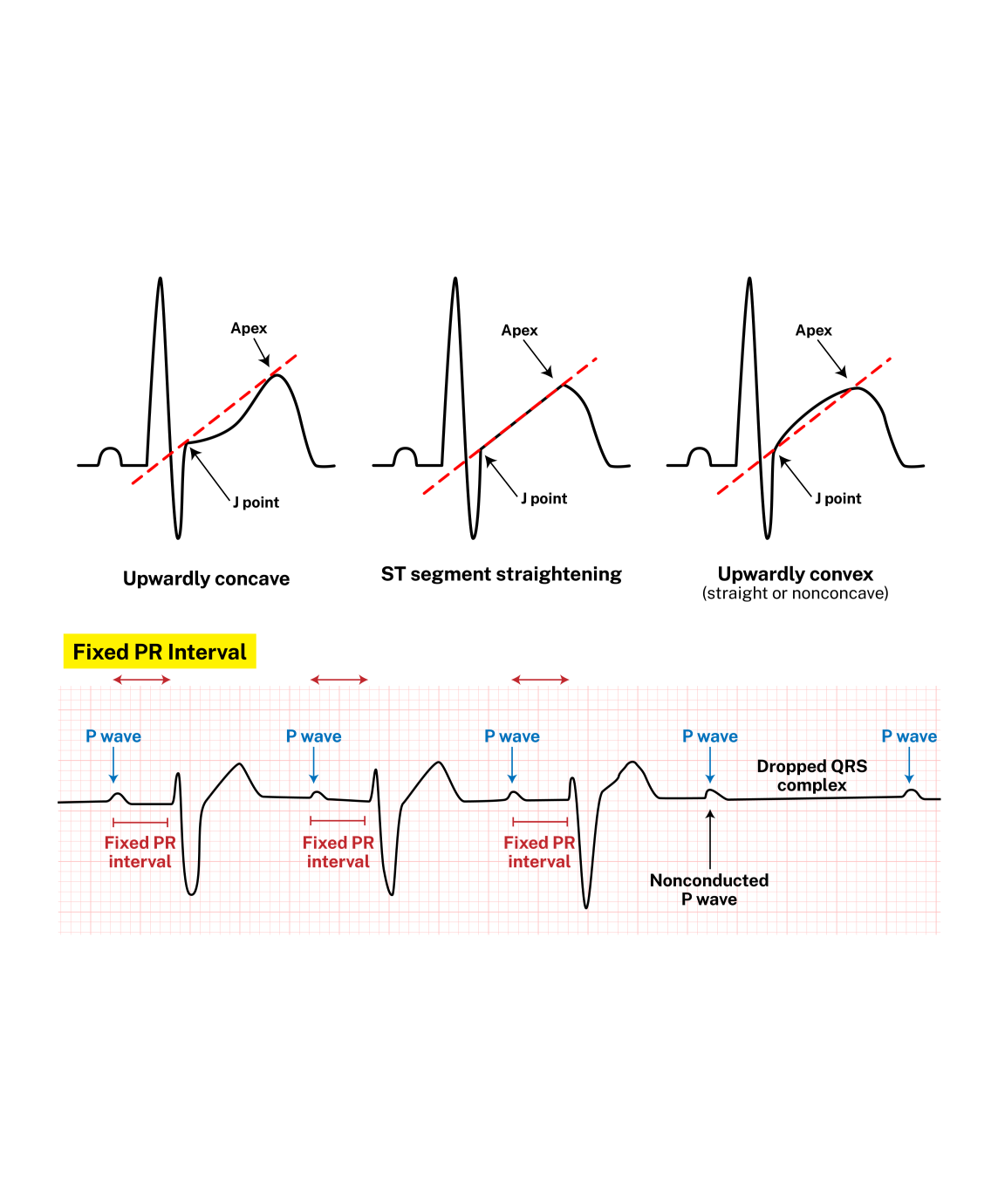
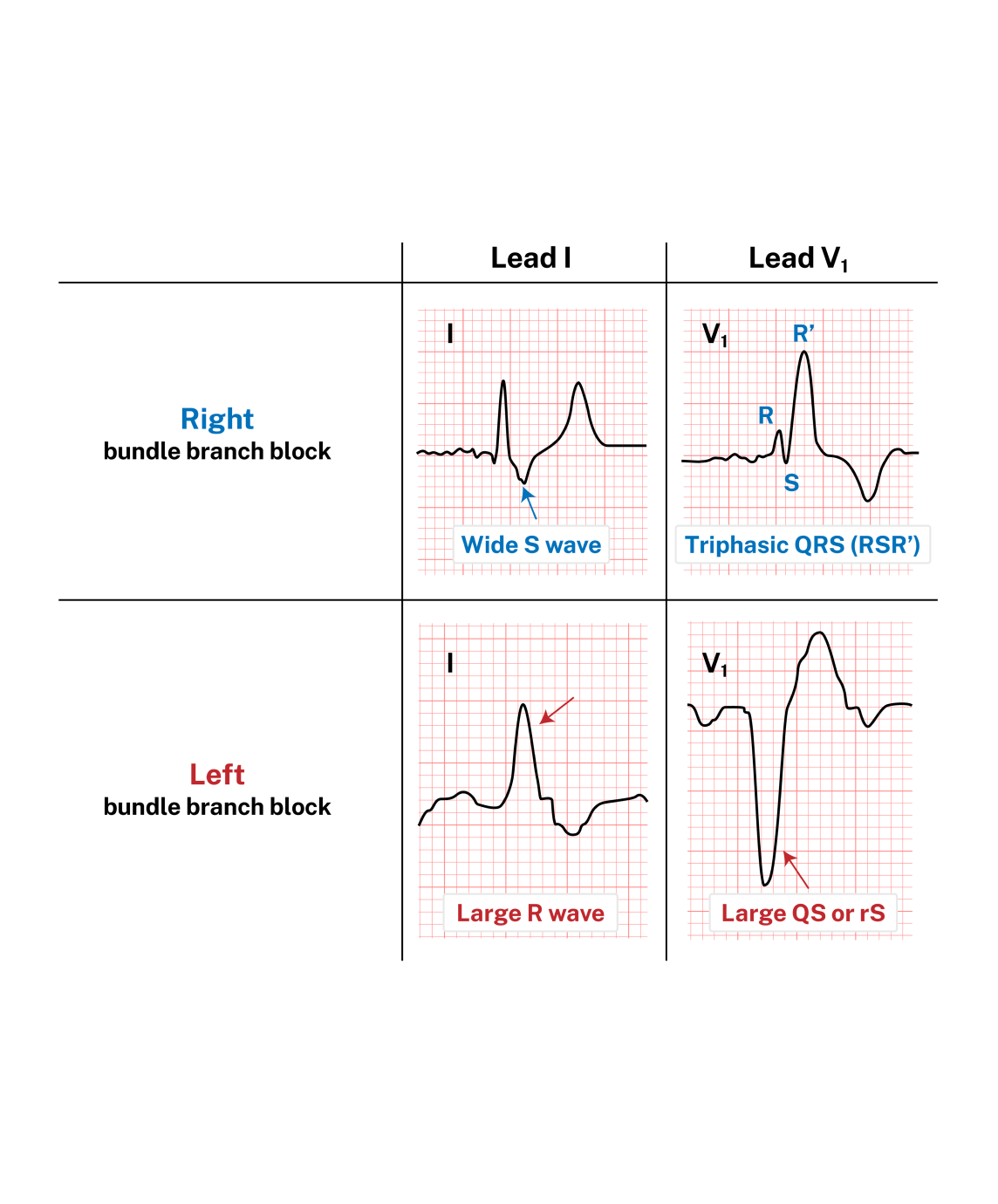
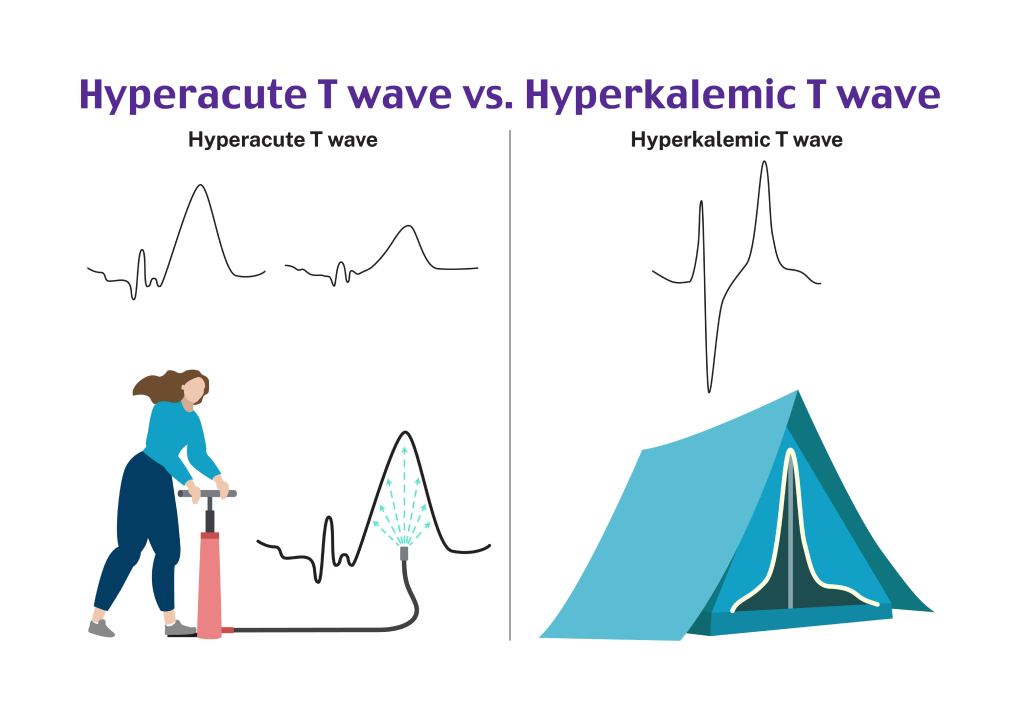
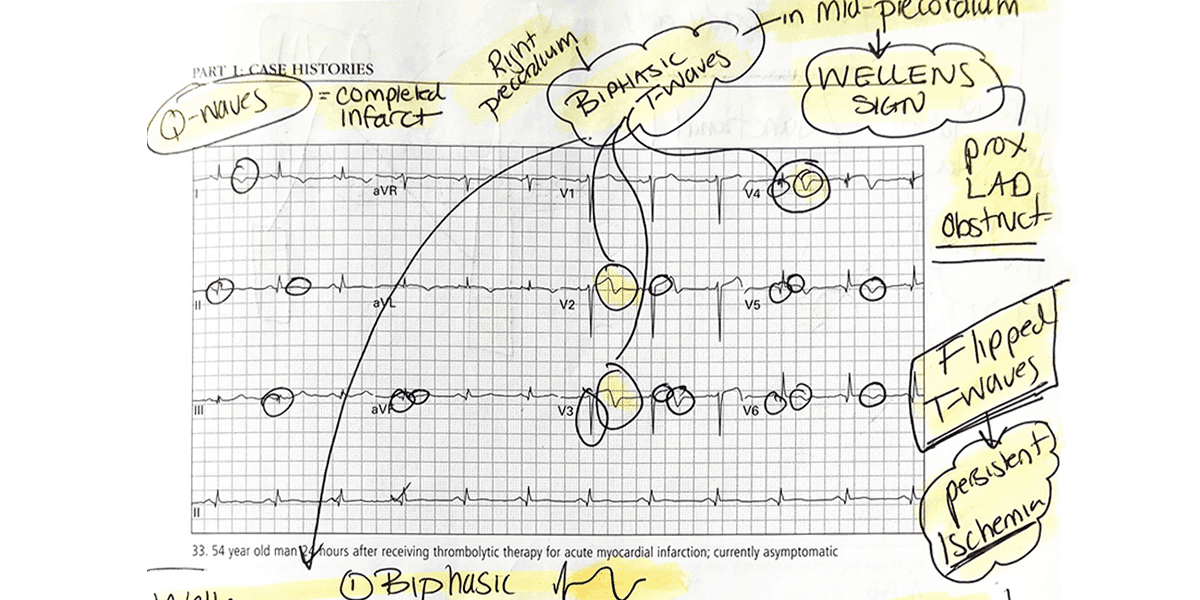
Read ECGs Better Than a Cardiologist
With a Qbank, strengthen your ECG-reading skills & be the person your colleagues turn to
Real ECGs,
Real Scenarios
Trade your flashcards for high-yield questions and explanations
Test your knowledge with real case studies and one-liners of context, allowing you to identify clues the same way you would in a real scenario.
All ECGs and questions were collected & created by Pendell Meyers, MD using content from his contributions to Dr. Smith’s ECG Blog.
Real ECGs, Real Scenarios
Be ready for the real patient
Build your knowledge with real cases & identify clues the same way you would at the bedside.
Read ECGs Better than a Cardiologist
Get 30-day, 90-day, or 365-day access to the ECG Qbank
From ECG to Cath Lab...
Find out if that STEMI was real
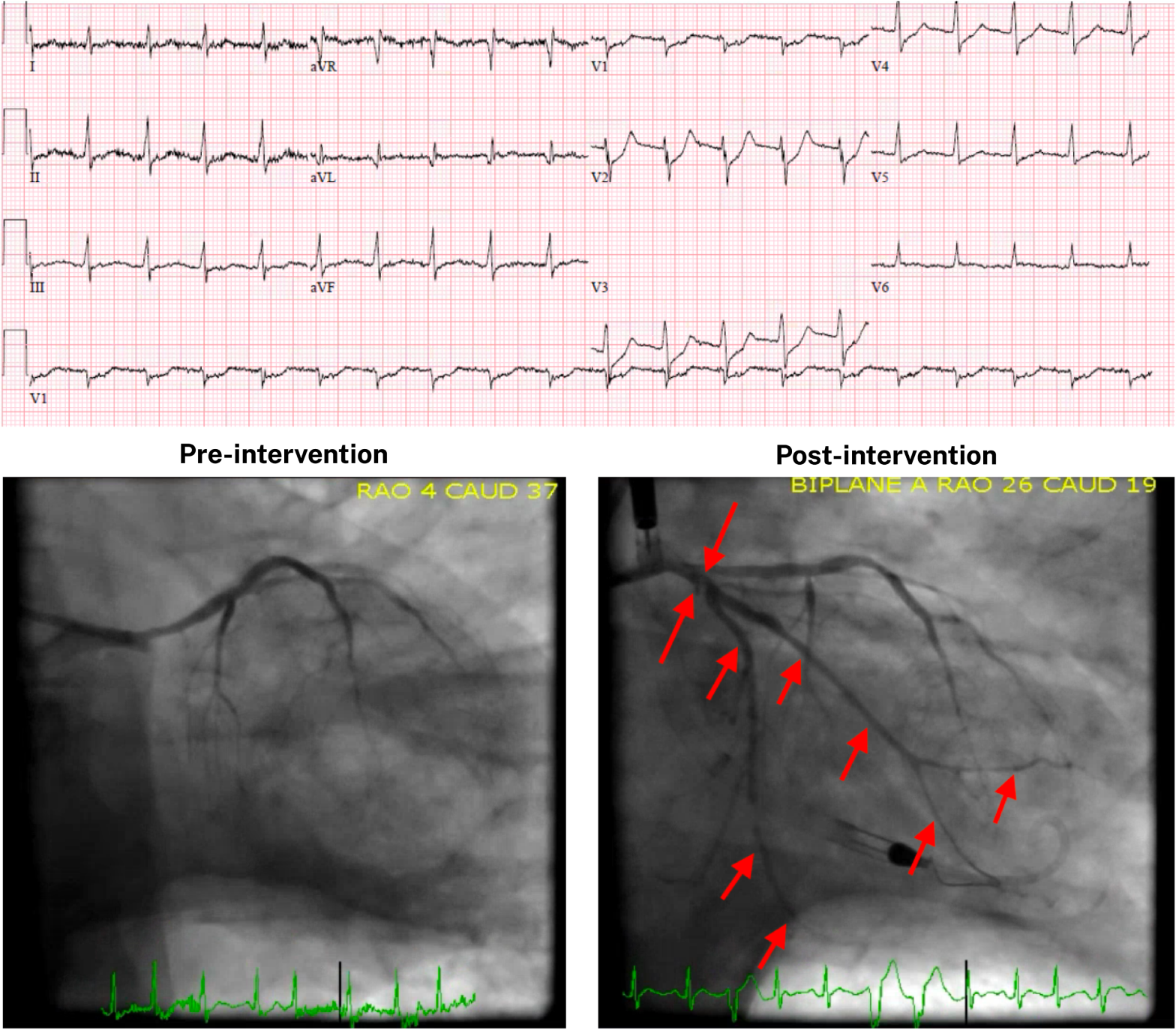
...All in Qbank Format.
A comprehensive guide for reading ECGs

Question
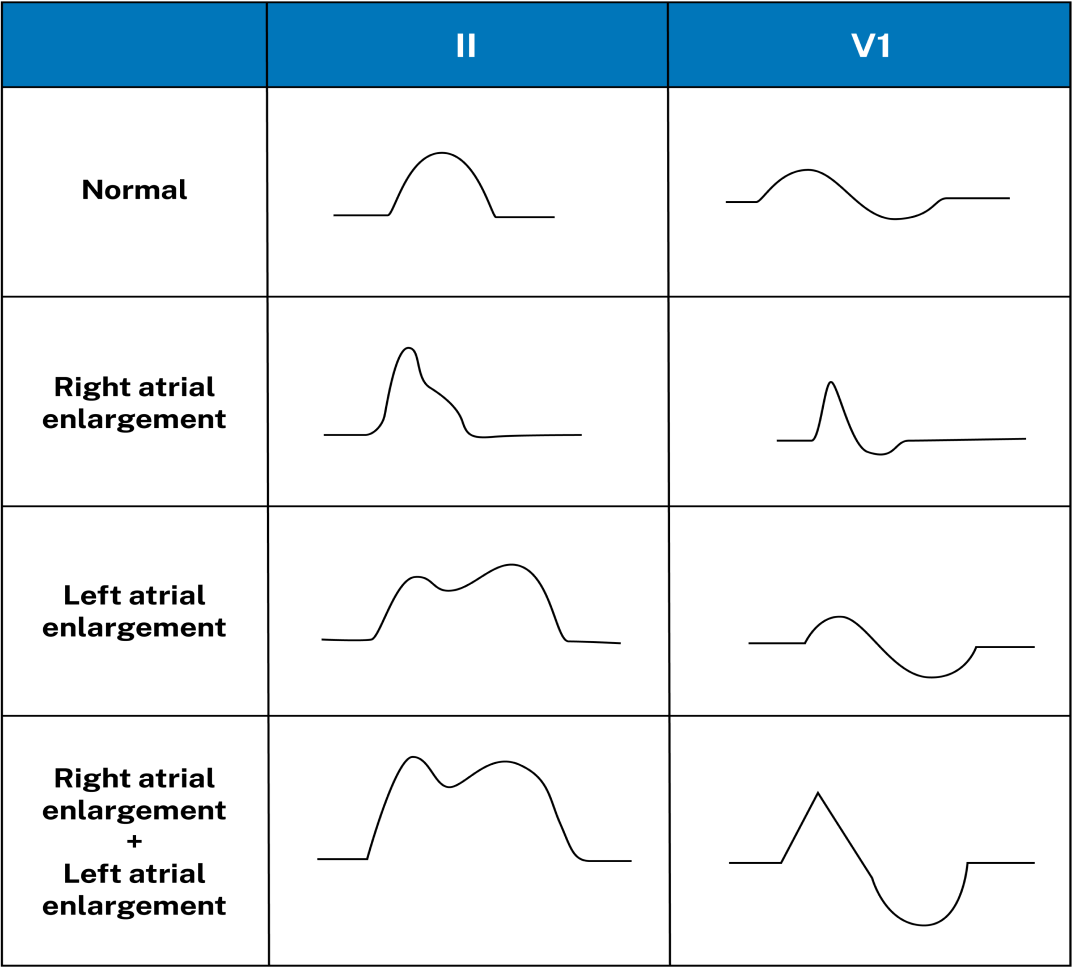
Which of the following best describes the morphology of normal sinus rhythm P waves?
Explanation
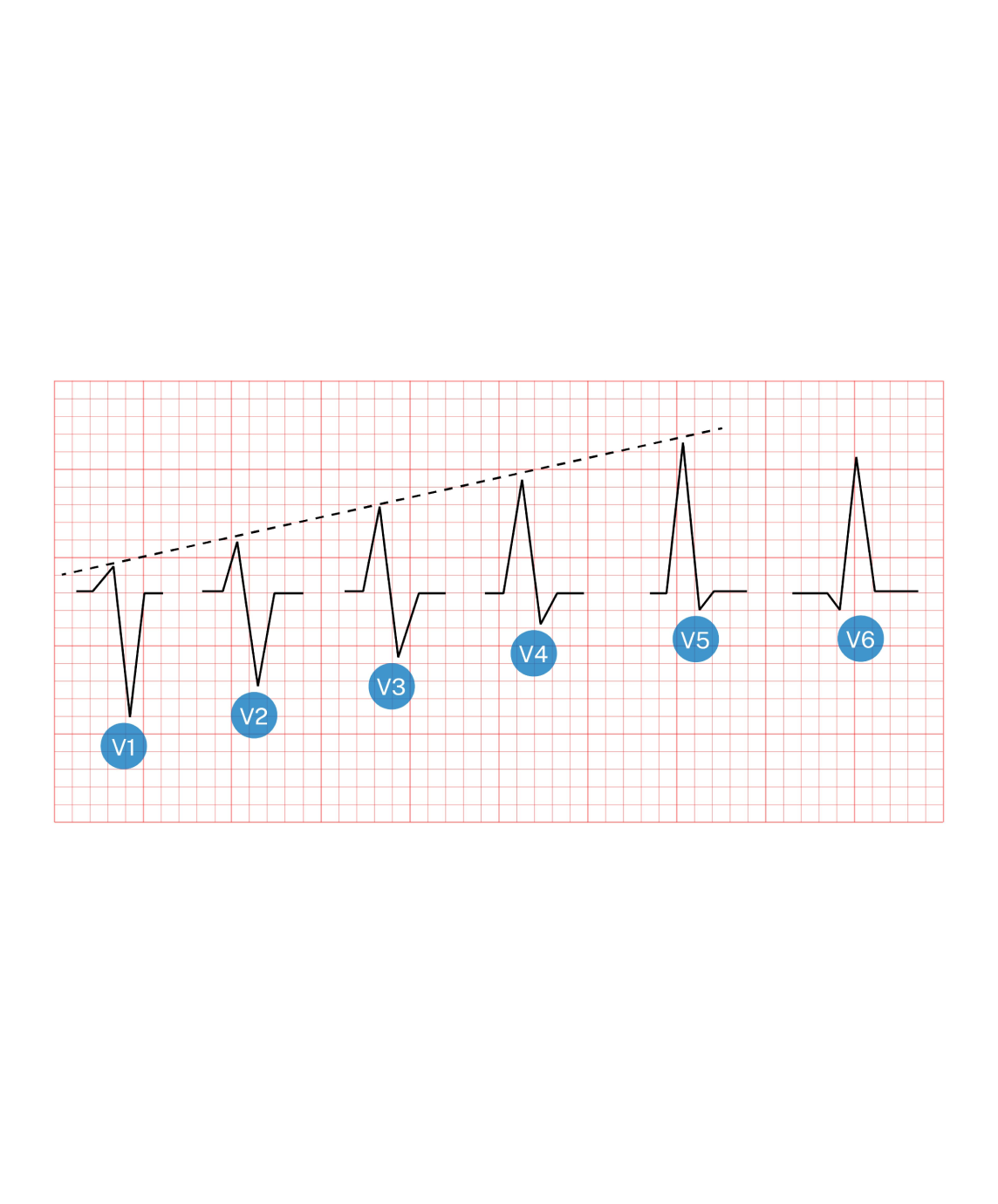
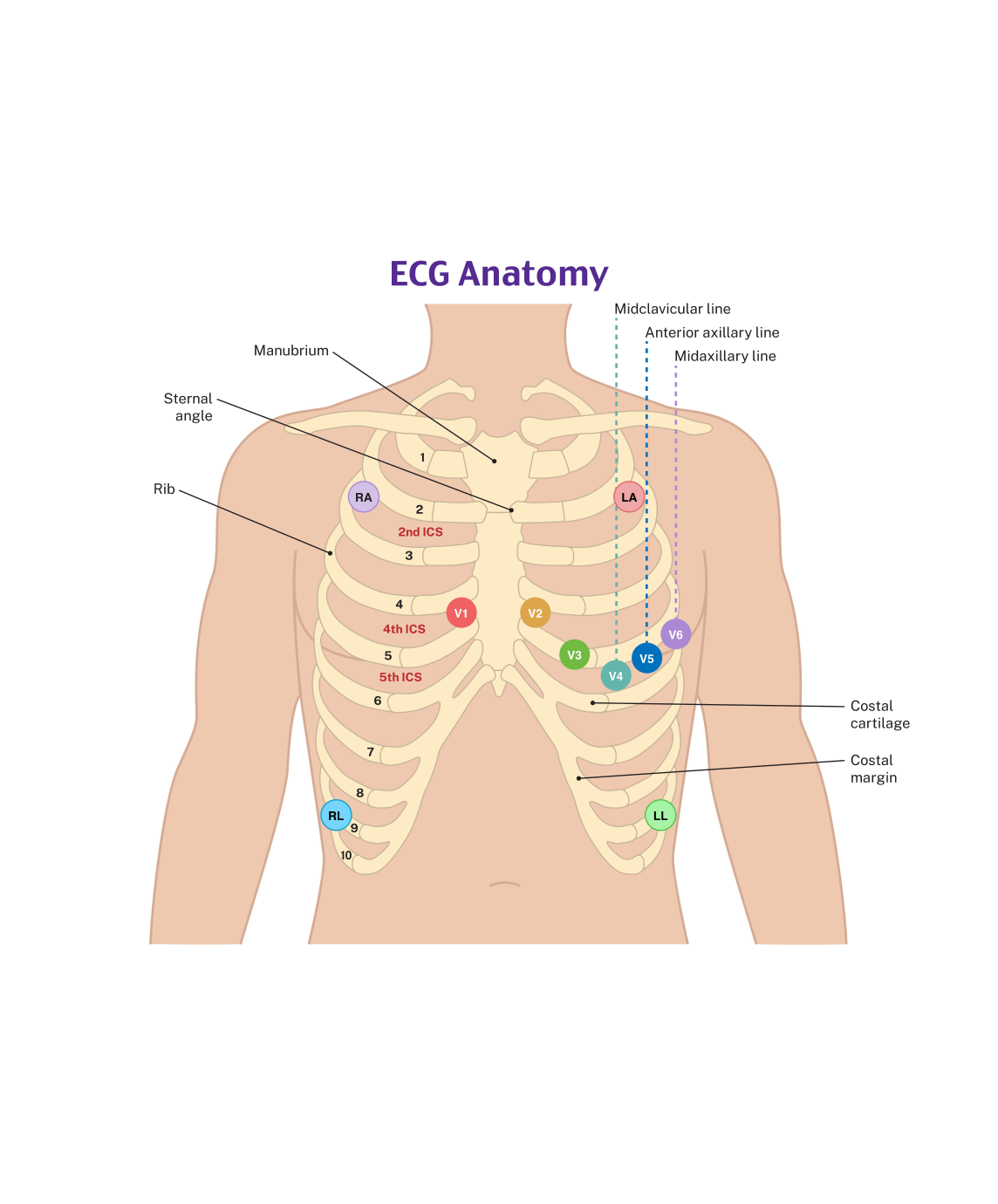
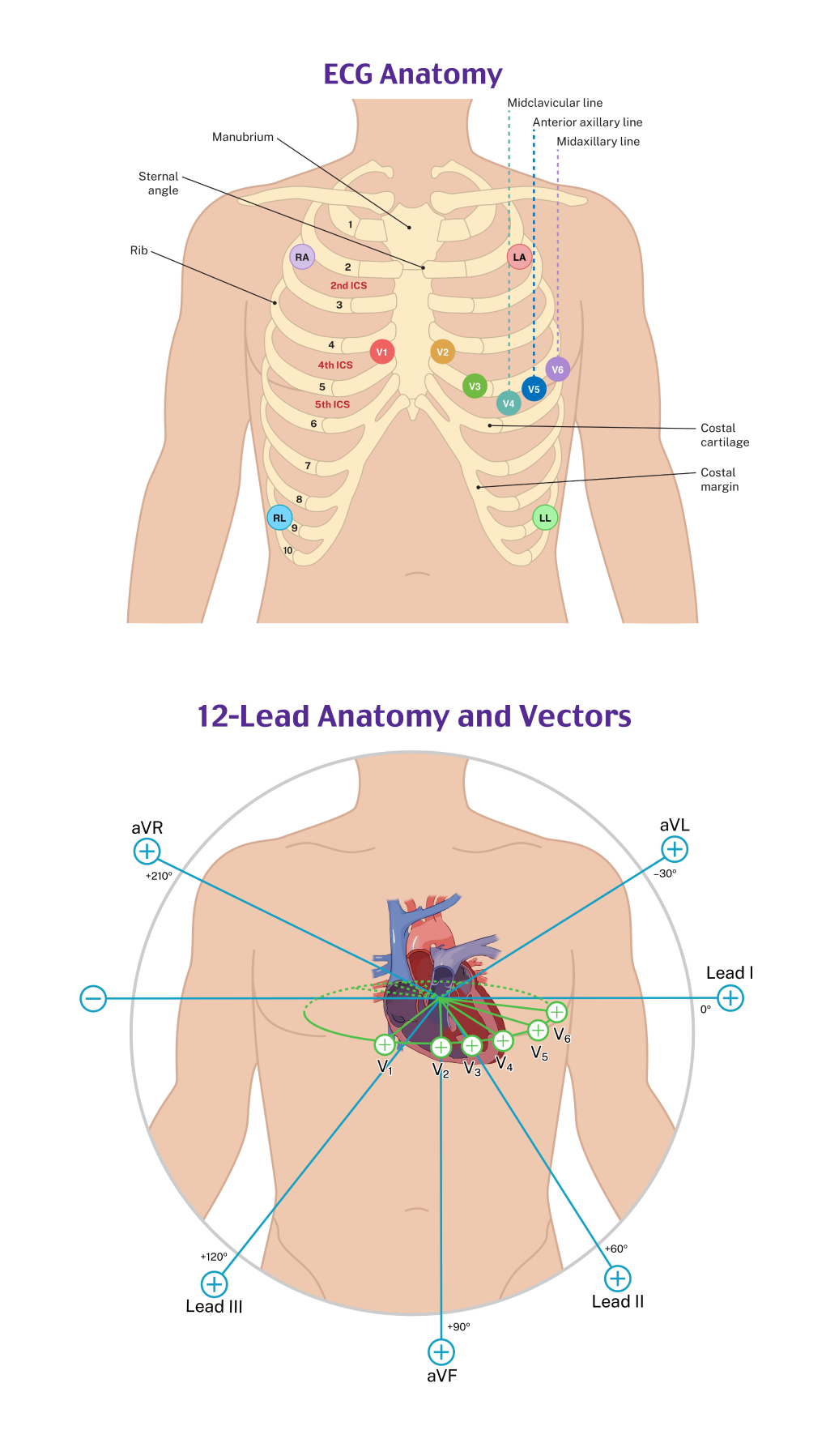
The P wave corresponds to atrial depolarization. The SA node is located in the right atrium near the superior vena cava, causing the direction of depolarization of normal P waves to be directed leftward and inferior, yielding upright (positive) P waves in most leads except aVR (which is oriented in the exact opposite direction). Because of the rightward placement of V1, the P wave is usually biphasic, with the initial positive deflection representing depolarization of the right atrium (toward the V1 electrode) and the subsequent negative depolarization representing the left atrium (away from the V1 electrode). Leads V1 and II are typically the best two leads for determining the P wave morphology and measurements, although this is not true in all cases.