Announcing the New Mock Pediatrics Shelf/Clerkship Exam

Introducing the Mock Pediatrics Shelf/Clerkship Exam, best suited for medical students who are looking to excel in their pediatrics clerkship.
The Mock Pediatrics Shelf/Clerkship Exam is located in your Boost Box (on the home page of your desktop/laptop Rosh Review account). It contains 100 questions and comprehensive explanations to help you prepare for the NBME Pediatrics Shelf Exam.
Categories covered in our pediatric shelf exam practice questions include topics such as allergic disorders, growth and development, and bacterial pathogens with a few “zebras” to keep you on your toes.
Here is an example of a question and explanation:
An 8-year-old boy presents to the office for new concerns of recurrent gross hematuria. He has no significant past medical or surgical history. Family history is significant for a maternal uncle “with some kidney issue” that mother cannot recall. Labs are ordered and are significant for a serum creatinine of 3.0 mg/dL. After consultation with a pediatric nephrologist, a renal biopsy is performed. The pathologic specimen shows splitting of the glomerular basement membrane and abnormal immunostaining for type IV collagen. What other finding is associated with this diagnosis?
A. Decreased olfaction
B. Hearing loss
C. Muscular cramping
D. Ventricular septal defect
Answer B
This 8-year-old boy has Alport syndrome, which is a genetic disease affecting the glomerular basement membrane due to a mutation in the type IV collagen gene. Alport syndrome can have an X-linked recessive transmission (such as this child), which accounts for a majority of the genetics of this disease. Autosomal recessive and dominant transmissions can also occur. The renal manifestations include microscopic hematuria and gross hematuria. Over time, patients progress to end-stage renal disease. This child has an elevated creatinine level. Diagnosis can be made by renal biopsy, which shows the characteristic pattern described above, and abnormal immunostaining of type IV collagen. Noninvasive diagnosis can be accomplished by molecular genetic testing to detect mutations in COL4A3, COL4A4, and COL4A5 genes that affect type IV collagen. Type IV collagen is also present in the cochlea, and bilateral sensorineural hearing loss is another common manifestation of this disease. Hearing loss also progressively worsens similar to the renal insufficiency.
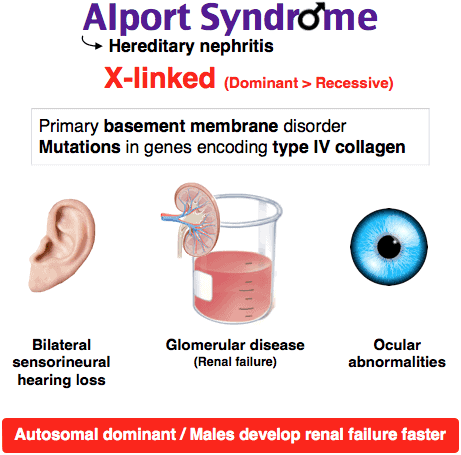
Decreased olfaction (A) is not associated with Alport syndrome, but ocular defects are seen. Anterior lenticonus and fleck retinopathy are specifically seen in this disease. Corneal involvement and cataracts are also common findings. Muscular cramping (C) is not a symptom of Alport syndrome, but leiomyomas have been reported in up to 5% of patients. These involve the smooth muscles of the uterus, respiratory system, and the gastrointestinal system. Ventricular septal defect (D) is not seen in patients with Alport syndrome, but arterial involvement in the form of aneurysms has been reported.
One Step Further question:
What would be the ultimate treatment in patients with Alport syndrome?
Answer:
Renal transplant.
We also have mock shelf exams available for emergency medicine, internal medicine, OB/GYN, family medicine, and psychiatry. And be sure to check out our pediatric board review question bank for thousands of comprehensive questions.
If you’re interested in How to Increase Your Pediatrics Certification or In-Training Exam Score by 50 Points and other tips, head over to the Rosh Blog.
Study on,
The Rosh Review Team





Comments (0)